Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) and quantitative real-time PCR (qPCR) have become essential tools in modern medical diagnostics. From detecting infectious diseases to monitoring genetic mutations, these technologies allow clinicians to obtain fast, accurate, and sensitive results that guide patient care.
What is PCR and qPCR in Medical Diagnostics?
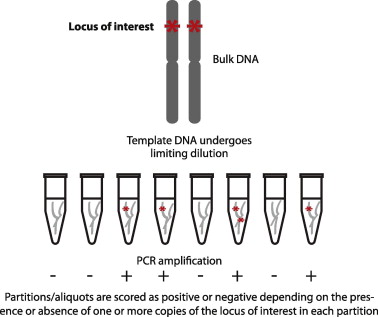
PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction) is a technique used to amplify specific DNA or RNA sequences, making it easier to detect even small amounts of genetic material. Read more
qPCR (quantitative PCR or real-time PCR) takes this a step further by quantifying the amplified DNA in real-time, providing both presence and amount of the target gene.
Applications in medicine include:
Infectious disease detection: Viruses (SARS-CoV-2, HIV), bacteria (TB, MRSA)
Genetic disorder screening: Cystic fibrosis, BRCA mutations
Cancer diagnostics: Detecting tumor-specific DNA or RNA
Monitoring treatment response: Tracking viral load or minimal residual disease
Advantages of qPCR in Medical Diagnostics
High Sensitivity: Detects very low amounts of pathogen DNA/RNA.
Rapid Results: qPCR can deliver results in hours instead of days.
Quantitative Data: Allows monitoring of viral load, gene expression, or disease progression.
Multiplexing: Can detect multiple targets in a single reaction.
Automation Compatible: Suitable for high-throughput diagnostic labs.
Common Medical Diagnostic Applications
1. Infectious Diseases
qPCR is widely used to detect and quantify pathogens in patient samples. For example, In agricultural research, PCR is routinely used to detect genetically modified organisms (GMOs) in crops, ensuring compliance with regulatory standards and monitoring food safety.
2. Genetic Screening
qPCR allows for rapid detection of genetic mutations responsible for inherited diseases, helping in early diagnosis and family counseling.
3. Cancer Biomarker Detection
Circulating tumor DNA (ctDNA) can be quantified using qPCR, providing insights into tumor burden and treatment effectiveness.
4. Personalized Medicine
qPCR helps tailor treatments based on gene expression profiles or mutation status, enabling precision medicine.
Challenges and Considerations
While PCR and qPCR are powerful, accuracy depends on proper sample collection, high-quality reagents, and careful experimental design. Common challenges include:
Contamination leading to false positives
Poor primer design affecting specificity
Sample degradation reducing sensitivity
Tip: Always include controls such as No Template Controls (NTC) and internal reference genes for reliable results.
Conclusion
qPCR and PCR are transforming the field of medical diagnostics by enabling rapid, sensitive, and quantitative detection of pathogens, genetic disorders, and cancer biomarkers. With proper technique, these tools improve patient outcomes and support personalized medicine.